|

by Dr. Tony Phillips
03.10.2006
from
ScienceNASA Website
March 10, 2006: It’s official: Solar minimum has arrived. Sunspots
have all but vanished. Solar flares are nonexistent. The sun is
utterly quiet.
Like the quiet before a storm...
This week researchers announced that a storm is coming--the most
intense solar maximum in fifty years. The prediction comes from a
team led by Mausumi Dikpati of the National Center for Atmospheric
Research (NCAR).
"The next sunspot cycle will be 30% to 50% stronger
than the previous one," she says.
If correct, the years ahead could
produce a burst of solar activity second only to the historic Solar
Max of 1958.
That was a solar maximum. The Space Age was just beginning: Sputnik
was launched in Oct. 1957 and Explorer 1 (the first US satellite) in
Jan. 1958. In 1958 you couldn’t tell that a solar storm was underway
by looking at the bars on your cell phone; cell phones didn’t exist.
Even so, people knew something big was happening when Northern
Lights were sighted three times in Mexico. A similar maximum now
would be noticed by its effect on cell phones, GPS, weather
satellites and many other modern technologies.

Intense auroras over
Fairbanks, Alaska, in 1958.
Dikpati’s prediction is unprecedented. In nearly-two centuries since
the 11-year sunspot cycle was discovered, scientists have struggled
to predict the size of future maxima—and failed. Solar maxima can be
intense, as in 1958, or barely detectable, as in 1805, obeying no
obvious pattern.
The key to the mystery, Dikpati realized years ago, is a conveyor
belt on the sun.
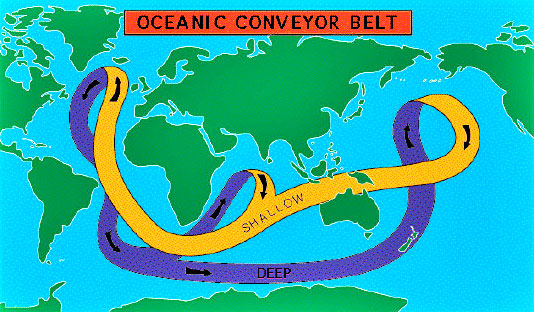
We have something similar here on Earth—the Great Ocean Conveyor
Belt, popularized in the sci-fi movie The Day After Tomorrow. It is
a network of currents that carry water and heat from ocean to ocean--see
the diagram below. In the movie, the Conveyor Belt stopped and threw
the world’s weather into chaos.
click above image
Earth’s "Great Ocean
Conveyor Belt."
The sun’s conveyor belt is a current, not of water, but of
electrically-conducting gas. It flows in a loop from the sun’s
equator to the poles and back again. Just as the Great Ocean
Conveyor Belt controls weather on Earth, this solar conveyor belt
controls weather on the sun. Specifically, it controls the sunspot
cycle.
Solar physicist David Hathaway of the National Space Science &
Technology Center (NSSTC) explains:
"First, remember what sunspots
are--tangled knots of magnetism generated by the sun’s inner dynamo.
A typical sunspot exists for just a few weeks. Then it decays,
leaving behind a ’corpse’ of weak magnetic fields."
Enter the conveyor belt
"The top of the conveyor belt skims the surface of the sun, sweeping
up the magnetic fields of old, dead sunspots. The ’corpses’ are
dragged down at the poles to a depth of 200,000 km where the sun’s
magnetic dynamo can amplify them. Once the corpses (magnetic knots)
are reincarnated (amplified), they become buoyant and float back to
the surface." Presto—new sunspots!
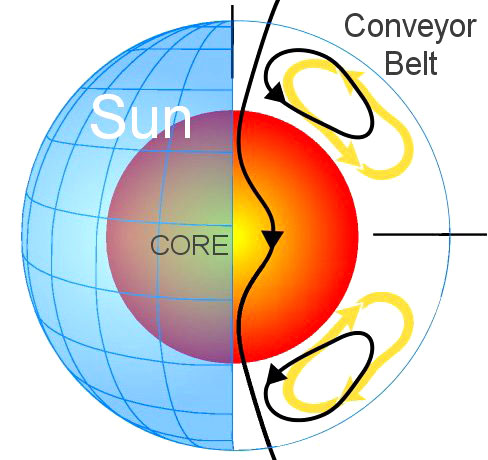
The sun’s
"great conveyor belt."
All this happens with massive slowness.
"It takes about 40 years for
the belt to complete one loop," says Hathaway. The speed varies "anywhere
from a 50-year pace (slow) to a 30-year pace (fast)."
When the belt is turning "fast," it means that lots of magnetic
fields are being swept up, and that a future sunspot cycle is going
to be intense. This is a basis for forecasting:
"The belt was
turning fast in 1986-1996," says Hathaway. "Old magnetic fields
swept up then should re-appear as big sunspots in 2010-2011."
Like most experts in the field, Hathaway has confidence in the
conveyor belt model and agrees with Dikpati that the next solar
maximum should be a doozy. But he disagrees with one point.
Dikpati’s forecast puts Solar Max at 2012. Hathaway believes it will
arrive sooner, in 2010 or 2011.
"History shows that big sunspot cycles
’ramp up’ faster than small
ones," he says. "I expect to see the first sunspots of the next
cycle appear in late 2006 or 2007—and Solar Max to be underway by
2010 or 2011."
Who’s right? Time will tell. Either way, a storm is coming.
|



