There are 64 hexagrams (kua) in the I Ching and there are 64 codons in the universal genetic code. The kua can be thought of as being composed of 3 symbols of 2 lines each. The codons are composed of 4 nucleic acids taken 3 at a time. The problem is: which nucleic acid corresponds to which I Ching symbol?
THE FOUR EMBLEMATIC SYMBOLS OR DIGRAMS
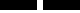
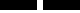


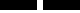


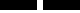 6 8 9 7 "Ritual" numbers
OLD YIN YOUNG YIN OLD YANG YOUNG YANG
THYMINE CYTOSINE ADENINE GUANINE Nucleic acids
\PYRIMIDINES/ \PURINES/
6 8 9 7 "Ritual" numbers
OLD YIN YOUNG YIN OLD YANG YOUNG YANG
THYMINE CYTOSINE ADENINE GUANINE Nucleic acids
\PYRIMIDINES/ \PURINES/
Note that the basic structure of the pyrimidine nucleic acids has 6 atoms
and that of the purine nucleic acids has 9. The Old Yang symbol has a
"ritual number" of 9 and Old Yin's ritual number is 6. Therefore I assign
the yang symbols to the purines and the yin symbols to the pyrimidines.
The next thing to determine is: which yang symbol (Old or Young) corresponds to which purine nucleic acid (Adenine or Guanine).
In the I Ching, yang is associated with energy and yin is associated with matter. Energy for all of the bio-chemical processes in the cell is provided by the chemical Adenosine Triphosphate. Its major component is, of course, the nucleic acid Adenine. Since yang=energy and Adenine is associated with cellular energy production; I assign Adenine to Old Yang because it has two yang lines. Because of the way the nucleic acids bond to each other in the DNA double helix molecule the other nucleic acid to symbol assignments follow logically from this first assignment.
Adenine bonds to Thymine with 2 hydrogen atoms and Guanine bonds to Cytosine with 3 hydrogen atoms. Old Yin is the complementary opposite of Old Yang. In the DNA double helix Thymine is always opposite Adenine; therefore it is assigned to Old Yin. (Note: The nucleic acid Uracil substitutes for Thymine in messenger RNA [mRNA].)
In the DNA double helix Guanine is always opposite Cytosine. Since Guanine is already assigned to Young Yang (because it is a purine nucleic acid); Cytosine must be assigned to Young Yin.